PyPI, the Python package index, provides a JSON API for information about its packages. This is essentially a machine-readable source of the same kind of data you can access while browsing the website. For example, as a human, I can head to the NumPy project page in my browser, click around, and see which versions there are, what files are available, and things like release dates and which Python versions are supported:
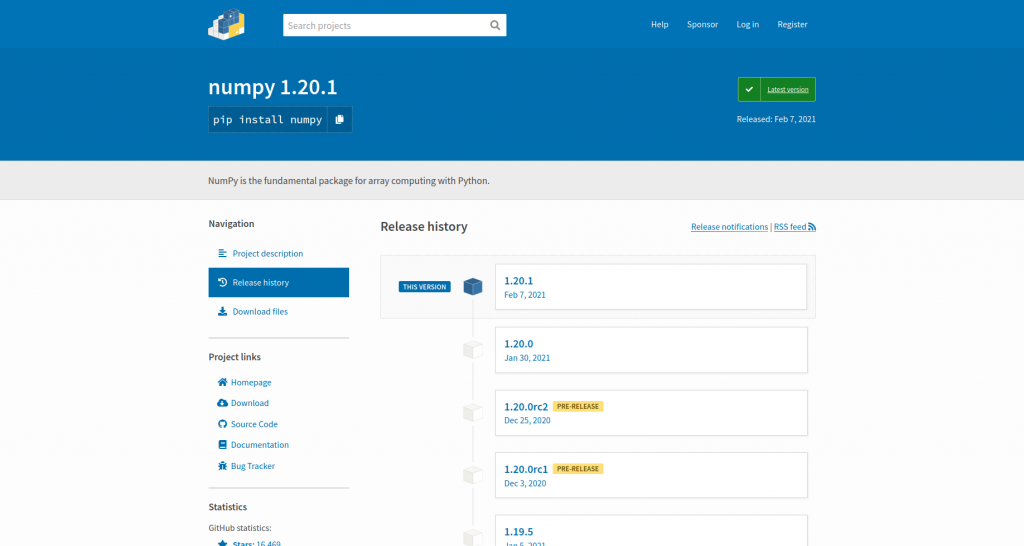
(Ben Nuttall, CC BY-SA 4.0)
But if I want to write a program to access this data, I can use the JSON API instead of having to scrape and parse the HTML on these pages.
As an aside: On the old PyPI website, when it was hosted at pypi.python.org, the NumPy project page was at pypi.python.org/pypi/numpy, and accessing the JSON was a simple matter of adding a /json on the end, hence https://pypi.org/pypi/numpy/json. Now the PyPI website is hosted at pypi.org, and NumPy's project page is at pypi.org/project/numpy. The new site doesn't include rendering the JSON, but it still runs as it was before. So now, rather than adding /json to the URL, you have to remember the URL where they are.
You can open up the JSON for NumPy in your browser by heading to its URL. Firefox renders it nicely like this:
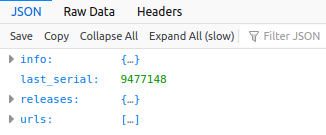
(Ben Nuttall, CC BY-SA 4.0)
You can open info, releases, and urls to inspect the contents within. Or you can load it into a Python shell. Here are a few lines to get started:
import requests
url = "https://pypi.org/pypi/numpy/json"
r = requests.get(url)
data = r.json()Once you have the data (calling .json() provides a dictionary of the data), you can inspect it:
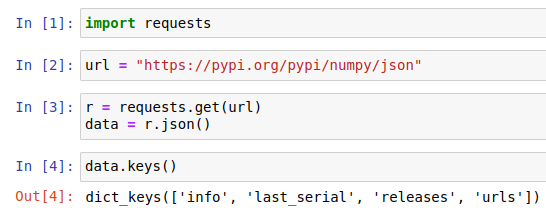
(Ben Nuttall, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Open releases, and inspect the keys inside it:
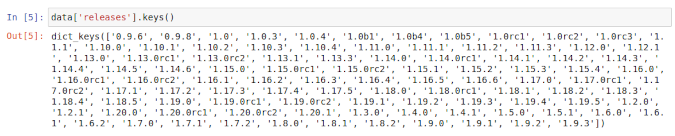
(Ben Nuttall, CC BY-SA 4.0)
This shows that releases is a dictionary with version numbers as keys. Pick one (say, the latest one) and inspect that:
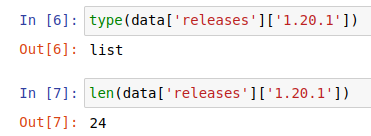
(Ben Nuttall, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Each release is a list, and this one contains 24 items. But what is each item? Since it's a list, you can index the first one and take a look:
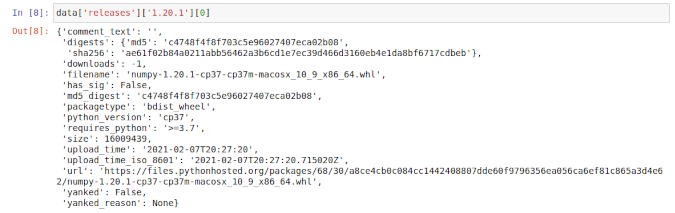
(Ben Nuttall, CC BY-SA 4.0)
This item is a dictionary containing details about a particular file. So each of the 24 items in the list relates to a file associated with this particular version number, i.e., the 24 files listed at https://pypi.org/project/numpy/1.20.1/#files.
You could write a script that looks for something within the available data. For example, the following loop looks for versions with sdist (source distribution) files that specify a requires_python attribute and prints them:
for version, files in data['releases'].items():
for f in files:
if f.get('packagetype') == 'sdist' and f.get('requires_python'):
print(version, f['requires_python'])
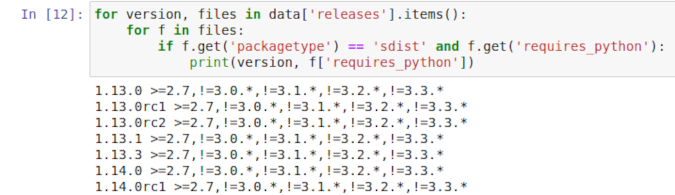
(Ben Nuttall, CC BY-SA 4.0)
piwheels
Last year I implemented a similar API on the piwheels website. piwheels.org is a Python package index that provides wheels (precompiled binary packages) for the Raspberry Pi architecture. It's essentially a mirror of the package set on PyPI, but with Arm wheels instead of files uploaded to PyPI by package maintainers.
Since piwheels mimics the URL structure of PyPI, you can change the pypi.org part of a project page's URL to piwheels.org. It'll show you a similar kind of project page with details about which versions we have built and which files are available. Since I liked how the old site allowed you to add /json to the end of the URL, I made ours work that way, so NumPy's project page on PyPI is pypi.org/project/numpy. On piwheels, it is piwheels.org/project/numpy, and the JSON is at piwheels.org/project/numpy/json.
There's no need to duplicate the contents of PyPI's API, so we provide information about what's available on piwheels and include a list of all known releases, some basic information, and a list of files we have:
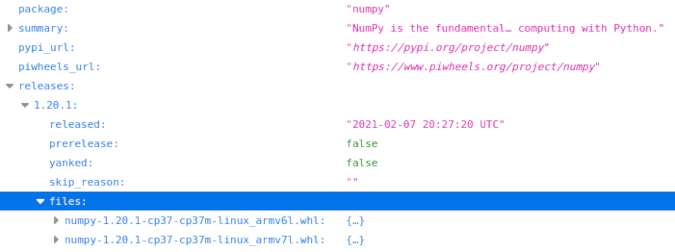
(Ben Nuttall, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Similar to the previous PyPI example, you could create a script to analyze the API contents, for example, to show the number of files piwheels has for each version of NumPy:
import requests
url = "https://www.piwheels.org/project/numpy/json"
package = requests.get(url).json()
for version, info in package['releases'].items():
if info['files']:
print('{}: {} files'.format(version, len(info['files'])))
else:
print('{}: No files'.format(version))Also, each file contains some metadata:
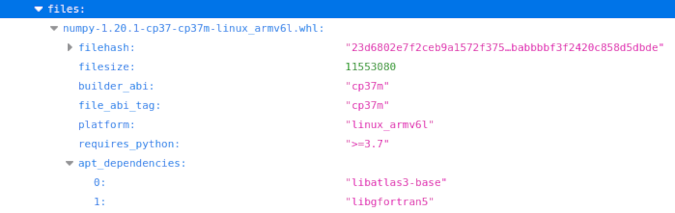
(Ben Nuttall, CC BY-SA 4.0)
One handy thing is the apt_dependencies field, which lists the Apt packages needed to use the library. In the case of this NumPy file, as well as installing NumPy with pip, you'll also need to install libatlas3-base and libgfortran using Debian's Apt package manager.
Here is an example script that shows the Apt dependencies for a package:
import requests
def get_install(package, abi):
url = 'https://piwheels.org/project/{}/json'.format(package)
r = requests.get(url)
data = r.json()
for version, release in sorted(data['releases'].items(), reverse=True):
for filename, file in release['files'].items():
if abi in filename:
deps = ' '.join(file['apt_dependencies'])
print("sudo apt install {}".format(deps))
print("sudo pip3 install {}=={}".format(package, version))
return
get_install('opencv-python', 'cp37m')
get_install('opencv-python', 'cp35m')
get_install('opencv-python-headless', 'cp37m')
get_install('opencv-python-headless', 'cp35m')We also provide a general API endpoint for the list of packages, which includes download stats for each package:
import requests
url = "https://www.piwheels.org/packages.json"
packages = requests.get(url).json()
packages = {
pkg: (d_month, d_all)
for pkg, d_month, d_all, *_ in packages
}
package = 'numpy'
d_month, d_all = packages[package]
print(package, "has had", d_month, "downloads in the last month")
print(package, "has had", d_all, "downloads in total")pip search
Since pip search is currently disabled due to its XMLRPC interface being overloaded, people have been looking for alternatives. You can use the piwheels JSON API to search for package names instead since the set of packages is the same:
#!/usr/bin/python3
import sys
import requests
PIWHEELS_URL = 'https://www.piwheels.org/packages.json'
r = requests.get(PIWHEELS_URL)
packages = {p[0] for p in r.json()}
def search(term):
for pkg in packages:
if term in pkg:
yield pkg
if __name__ == '__main__':
if len(sys.argv) == 2:
results = search(sys.argv[1].lower())
for res in results:
print(res)
else:
print("Usage: pip_search TERM")For more information, see the piwheels JSON API documentation.
This article originally appeared on Ben Nuttall's Tooling Tuesday blog and is reused with permission.












1 Comment