Modern computers are ever increasing in performance and capacity. This matters little if that increasing capacity is not well utilized. Following is a description of the motivation and work behind "curt," a new tool for Linux systems for measuring and breaking down system utilization by process, by task, and by CPU using the perf command's Python scripting capabilities.
I had the privilege of presenting this topic at Texas Linux Fest 2018, and here I've gone a bit deeper into the details, included links to further information, and expanded the scope of my talk.
System utilization
In discussing computation, let's begin with some assertions:
- Every computational system is equally fast at doing nothing.
- Computational systems were created to do things.
- A computational system is better at doing things when it is doing something than when it is doing nothing.
Modern computational systems have many streams of execution:
- Often, very large systems are created by literally wiring together smaller systems. At IBM, these smaller systems are sometimes called CECs (short for Central Electronics Complexes and pronounced "keks").
- There are multiple sockets for processor modules in each system.
- There are sometimes multiple chips per socket (in the form of dual-chip modules—DCMs—or multi-chip modules—MCMs).
- There are multiple cores per chip.
- There are multiple threads per core.
In sum, there are potentially thousands of execution threads across a single computational system.
Ideally, all these execution streams are 100% busy doing useful work. One measure of utilization for an individual execution stream (CPU thread) is the percentage of time that thread has tasks scheduled and running. (Note that I didn't say "doing useful work." Creating a tool that measures useful work is left as an exercise for the reader.) By extension, system utilization is the overall percentage of time that all execution streams of a system have tasks scheduled and running. Similarly, utilization can be defined with respect to an individual task. Task utilization is the percentage of the lifetime of the task that was spent actively running on any CPU thread. By extension, process utilization is the collective utilization of its tasks.
Utilization measurement tools
There are tools that measure system utilization: uptime, vmstat, mpstat, nmon, etc. There are tools that measure individual process utilization: time. There are not many tools that measure system-wide per-process and per-task utilization. One such command is curt on AIX. According to IBM's Knowledge Center: "The curt command takes an AIX trace file as input and produces a number of statistics related to processor (CPU) utilization and process/thread/pthread activity."
The AIX curt command reports system-wide, per-processor, per-process, and per-task statistics for application processing (user time), system calls (system time), hypervisor calls, kernel threads, interrupts, and idle time.
This seems like a good model for a similar command for a Linux system.
Utilization data
Before starting to create any tools for utilization analysis, it is important to know what data is required. Since utilization is directly related to whether a task is actively running or not, related scheduling events are required: When is the task made to run, and when is it paused? Tracking on which CPU the task runs is important, so migration events are required for implicit migrations. There are also certain system calls that force explicit migrations. Creation and deletion of tasks are obviously important. Since we want to understand user time, system time, hypervisor time, and interrupt time, events that show the transitions between those task states are required.
The Linux kernel contains "tracepoints" for all those events. It is possible to enable tracing for those events directly in the kernel's debugfs filesystem, usually mounted at /sys/kernel/debug, in the tracing directory (/sys/kernel/debug/tracing).
An easier way to record tracing data is with the Linux perf command.
The perf command
perf is a very powerful userspace command for tracing or counting both hardware and software events.
Software events are predefined in the kernel, can be predefined in userspace code, and can be dynamically created (as "probes") in kernel or userspace code.
perf can do much more than just trace and count, though.
perf stat
The stat subcommand of perf will run a command, count some events commonly found interesting, and produce a simple report:
Performance counter stats for './load 100000':
90537.006424 task-clock:u (msec) # 1.000 CPUs utilized
0 context-switches:u # 0.000 K/sec
0 cpu-migrations:u # 0.000 K/sec
915 page-faults:u # 0.010 K/sec
386,836,206,133 cycles:u # 4.273 GHz (66.67%)
3,488,523,420 stalled-cycles-frontend:u # 0.90% frontend cycles idle (50.00%)
287,222,191,827 stalled-cycles-backend:u # 74.25% backend cycles idle (50.00%)
291,102,378,513 instructions:u # 0.75 insn per cycle
# 0.99 stalled cycles per insn (66.67%)
43,730,320,236 branches:u # 483.010 M/sec (50.00%)
822,030,340 branch-misses:u # 1.88% of all branches (50.00%)
90.539972837 seconds time elapsedperf record, perf report, and perf annotate
For much more interesting analysis, the perf command can also be used to record events and information associated with the task state at the time the event occurred:
$ perf record ./some-command
[ perf record: Woken up 55 times to write data ]
[ perf record: Captured and wrote 13.973 MB perf.data (366158 samples) ]
$ perf report --stdio --show-nr-samples --percent-limit 4
# Samples: 366K of event 'cycles:u'
# Event count (approx.): 388851358382
#
# Overhead Samples Command Shared Object Symbol
# ........ ............ ....... ................. ................................................
#
62.31% 228162 load load [.] main
19.29% 70607 load load [.] sum_add
18.33% 67117 load load [.] sum_subThis example shows a program that spends about 60% of its running time in the function main and about 20% each in subfunctions sum_sub and sum_add. Note that the default event used by perf record is "cycles." Later examples will show how to use perf record with other events.
perf report can further report runtime statistics by source code line (if the compilation was performed with the -g flag to produce debug information):
$ perf report --stdio --show-nr-samples --percent-limit 4 --sort=srcline
# Samples: 366K of event 'cycles:u'
# Event count (approx.): 388851358382
#
# Overhead Samples Source:Line
# ........ ............ ...................................
#
19.40% 71031 load.c:58
16.16% 59168 load.c:18
15.11% 55319 load.c:14
13.30% 48690 load.c:66
13.23% 48434 load.c:70
4.58% 16767 load.c:62
4.01% 14677 load.c:56Further, perf annotate can show statistics for each instruction of the program:
$ perf annotate --stdio
Percent | Source code & Disassembly of load for cycles:u (70607 samples)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
: 0000000010000774 <sum_add>:
: int sum_add(int sum, int value) {
12.60 : 10000774: std r31,-8(r1)
0.02 : 10000778: stdu r1,-64(r1)
0.00 : 1000077c: mr r31,r1
41.90 : 10000780: mr r10,r3
0.00 : 10000784: mr r9,r4
0.05 : 10000788: stw r10,32(r31)
23.78 : 1000078c: stw r9,36(r31)
: return (sum + value);
0.76 : 10000790: lwz r10,32(r31)
0.00 : 10000794: lwz r9,36(r31)
14.75 : 10000798: add r9,r10,r9
0.00 : 1000079c: extsw r9,r9
: }
6.09 : 100007a0: mr r3,r9
0.02 : 100007a4: addi r1,r31,64
0.03 : 100007a8: ld r31,-8(r1)
0.00 : 100007ac: blr(Note: this code is not optimized.)
perf top
Similar to the top command, which displays (at a regular update interval) the processes using the most CPU time, perf top will display the functions using the most CPU time among all processes on the system, a nice leap in granularity.
perf list
The examples thus far have used the default event, run cycles. There are hundreds and perhaps thousands of events of different types. perf list will show them all. Following are just a few examples:
$ perf list
instructions [Hardware event]
context-switches OR cs [Software event]
L1-icache-loads [Hardware cache event]
mem_access OR cpu/mem_access/ [Kernel PMU event]
cache:
pm_data_from_l2
[The processor's data cache was reloaded from local core's L2 due to a demand load]
floating point:
pm_fxu_busy
[fxu0 busy and fxu1 busy]
frontend:
pm_br_mpred_cmpl
[Number of Branch Mispredicts]
memory:
pm_data_from_dmem
[The processor's data cache was reloaded from another chip's memory on the same Node or Group (Distant) due to a demand load]
pm_data_from_lmem
[The processor's data cache was reloaded from the local chip's Memory due to a demand load]
rNNN [Raw hardware event descriptor]
raw_syscalls:sys_enter [Tracepoint event]
syscalls:sys_enter_chmod [Tracepoint event]
sdt_libpthread:pthread_create [SDT event]Events labeled as Hardware event, Hardware cache event, Kernel PMU event, and most (if not all) of the events under the categories like cache, floating point, frontend, and memory are hardware events counted by the hardware and triggered each time a certain count is reached. Once triggered, an entry is made into the kernel trace buffer with the current state of the associated task. Raw hardware event codes are alphanumeric encodings of the hardware events. These are mostly needed when the hardware is newer than the kernel and the user needs to enable events that are new for that hardware. Users will rarely, if ever, need to use raw event codes.
Events labeled Tracepoint event are embedded in the kernel. These are triggered when that section of code is executed by the kernel. There are "syscalls" events for every system call supported by the kernel. raw_syscalls events are triggered for every system call. Since there is a limit to the number of events being actively traced, the raw_syscalls events may be more practical when a large number of system calls need to be traced.
Events labeled SDT event are for software-defined tracepoints (SDTs). These can be embedded in application or library code and enabled as needed. When enabled, they behave just like other events: When that section of code is executed (by any task being traced on the system), an entry is made in the kernel trace buffer with the current state of the associated task. This is a very powerful capability that can prove very useful.
perf buildid-cache and perf probe
Enabling SDTs is easy. First, make the SDTs for a certain library known to perf:
$ perf buildid-cache -v --add /lib/powerpc64le-linux-gnu/libpthread.so.0
$ perf list | grep libpthread
[…]
sdt_libpthread:pthread_create [SDT event]
[…]Then, turn SDT definitions into available tracepoints:
$ /usr/bin/sudo perf probe sdt_libpthread:pthread_create
Added new event:
sdt_libpthread:pthread_create (on %pthread_create in /lib/powerpc64le-linux-gnu/libpthread-2.27.so)
You can now use it in all perf tools, such as:
perf record -e sdt_libpthread:pthread_create -aR sleep 1
$ perf record -a -e sdt_libpthread:pthread_create ./test
[ perf record: Woken up 1 times to write data ]
[ perf record: Captured and wrote 0.199 MB perf.data (9 samples) ]Note that any location in an application or library can be made into a tracepoint. To find functions in an application that can be made into tracepoints, use perf probe with –funcs:
$ perf probe –x ./load --funcs
[…]
main
sum_add
sum_subTo enable the function main of the ./load application as a tracepoint:
/usr/bin/sudo perf probe –x ./load main
Added new event:
probe_load:main (on main in /home/pc/projects/load-2.1pc/load)
You can now use it in all perf tools, such as:
perf record –e probe_load:main –aR sleep 1
$ perf list | grep load:main
probe_load:main [Tracepoint event]
$ perf record –e probe_load:main ./load
[ perf record: Woken up 1 times to write data ]
[ perf record: Captured and wrote 0.024 MB perf.data (1 samples) ]perf script
Continuing the previous example, perf script can be used to walk through the perf.data file and output the contents of each record:
$ perf script
Load 16356 [004] 80526.760310: probe_load:main: (4006a2)Processing perf trace data
The preceding discussion and examples show that perf can collect the data required for system utilization analysis. However, how can that data be processed to produce the desired results?
perf eBPF
A relatively new and emerging technology with perf is called eBPF. BPF is an acronym for Berkeley Packet Filter, and it is a C-like language originally for, not surprisingly, network packet filtering in the kernel. eBPF is an acronym for extended BPF, a similar, but more robust C-like language based on BPF.
Recent versions of perf can be used to incorporate compiled eBPF code into the kernel to securely and intelligently handle events for any number of purposes, with some limitations.
The capability is very powerful and quite useful for real-time, continuous updates of event-related data and statistics.
However, as this capability is emerging, support is mixed on current releases of Linux distributions. It's a bit complicated (or, put differently, I have not figured it out yet). It's also only for online use; there is no offline capability. For these reasons, I won't cover it further here.
perf data file
perf record produces a perf.data file. The file is a structured binary file, is not particularly well documented, has no programming interface for access, and is unclear on what compatibility guarantees exist. For these reasons, I chose not to directly use the perf.data file.
perf script
One of the last examples above showed how perf script is used for walking through the perf.data file and emitting basic information about each record there. This is an appropriate model for what would be needed to process the file and track the state changes and compute the statistics required for system utilization analysis.
perf script has several modes of operation, including several higher-level scripts that come with perf that produce statistics based on the trace data in a perf.data file.
$ perf script -l
List of available trace scripts:
rw-by-pid system-wide r/w activity
rwtop [interval] system-wide r/w top
wakeup-latency system-wide min/max/avg wakeup latency
failed-syscalls [comm] system-wide failed syscalls
rw-by-file <comm> r/w activity for a program, by file
failed-syscalls-by-pid [comm] system-wide failed syscalls, by pid
intel-pt-events print Intel PT Power Events and PTWRITE
syscall-counts-by-pid [comm] system-wide syscall counts, by pid
export-to-sqlite [database name] [columns] [calls] export perf data to a sqlite3 database
futex-contention futext contention measurement
sctop [comm] [interval] syscall top
event_analyzing_sample analyze all perf samples
net_dropmonitor display a table of dropped frames
compaction-times [-h] [-u] [-p|-pv] [-t | [-m] [-fs] [-ms]] [pid|pid-range|comm-regex] display time taken by mm compaction
export-to-postgresql [database name] [columns] [calls] export perf data to a postgresql database
stackcollapse produce callgraphs in short form for scripting use
netdev-times [tx] [rx] [dev=] [debug] display a process of packet and processing time
syscall-counts [comm] system-wide syscall counts
sched-migration sched migration overview
$ perf script failed-syscalls-by-pid /bin/ls
syscall errors:
comm [pid] count
------------------------------ ----------
ls [18683]
syscall: access
err = ENOENT 1
syscall: statfs
err = ENOENT 1
syscall: ioctl
err = ENOTTY 3What do these scripts look like? Let's find out.
$ locate failed-syscalls-by-pid
/usr/libexec/perf-core/scripts/python/failed-syscalls-by-pid.py
[…]
$ rpm –qf /usr/libexec/perf-core/scripts/python/failed-syscalls-by-pid.py
perf-4.14.0-46.el7a.x86_64
$ $ ls /usr/libexec/perf-core/scripts
perl python
$ perf script -s lang
Scripting language extensions (used in perf script -s [spec:]script.[spec]):
Perl [Perl]
pl [Perl]
Python [Python]
py [Python]So, these scripts come with perf, and both Python and Perl are supported languages.
Note that for the entirety of this content, I will refer exclusively to Python.
perf scripts
How do these scripts do what they do? Here are important extracts from /usr/libexec/perf-core/scripts/python/failed-syscalls-by-pid.py:
def raw_syscalls__sys_exit(event_name, context, common_cpu,
common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm,
common_callchain, id, ret):
[…]
if ret < 0:
[…]
syscalls[common_comm][common_pid][id][ret] += 1The function raw_syscalls__sys_exit has parameters for all the data for the associated event. The rest of the function only increments a counter associated with the command, process ID, and system call. The rest of the code doesn't do that much. Most of the complexity is in the function signature for the event-handling routine.
Fortunately, perf makes it easy to figure out the proper signatures for various tracepoint event-handling functions.
perf script –gen-script
For the raw_syscalls events, we can generate a trace containing just those events:
$ perf list | grep raw_syscalls
raw_syscalls:sys_enter [Tracepoint event]
raw_syscalls:sys_exit [Tracepoint event]
$ perf record -e 'raw_syscalls:*' /bin/ls >/dev/null
[ perf record: Woken up 1 times to write data ]
[ perf record: Captured and wrote 0.025 MB perf.data (176 samples) ]We can then have perf generate a script that contains sample implementations of event-handling functions for the events in the perf.data file:
$ perf script --gen-script python
generated Python script: perf-script.pyWhat do we find in the script?
def raw_syscalls__sys_exit(event_name, context, common_cpu,
common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm,
common_callchain, id, ret):
[…]
def raw_syscalls__sys_enter(event_name, context, common_cpu,
common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm,
common_callchain, id, args):Both event-handling functions are specified with their signatures. Nice!
Note that this script works with perf script –s:
$ perf script -s ./perf-script.py
in trace_begin
raw_syscalls__sys_exit 7 94571.445908134 21117 ls id=0, ret=0
raw_syscalls__sys_enter 7 94571.445942946 21117 ls id=45, args=���?bc���?�
[…]Now we have a template on which to base writing a Python script to parse the events of interest for reporting system utilization.
perf scripting
The Python scripts generated by perf script –gen-script are not directly executable. They must be invoked by perf:
$ perf script –s ./perf-script.pyWhat's really going on here?
- First,
perfstarts. Thescriptsubcommand's-soption indicates that an external script will be used. perfestablishes a Python runtime environment.perfloads the specified script.perfruns the script. The script can perform normal initialization and even handle command line arguments, although passing the arguments is slightly awkward, requiring a--separator between the arguments forperfand for the script:
$ perf script -s ./perf-script.py -- --script-arg1 [...]perfprocesses each record of the trace file, calling the appropriate event-handling function in the script. Those event-handling functions can do whatever they need to do.
Utilization
It appears that perf scripting has sufficient capabilities for a workable solution. What sort of information is required to generate the statistics for system utilization?
- Task creation (
fork,pthread_create) - Task termination (
exit) - Task replacement (
exec) - Task migration, explicit or implicit, and current CPU
- Task scheduling
- System calls
- Hypervisor calls
- Interrupts
It can be helpful to understand what portion of time a task spends in various system calls, handling interrupts, or making explicit calls out to the hypervisor. Each of these categories of time can be considered a "state" for the task, and the methods of transitioning from one state to another need to be tracked:
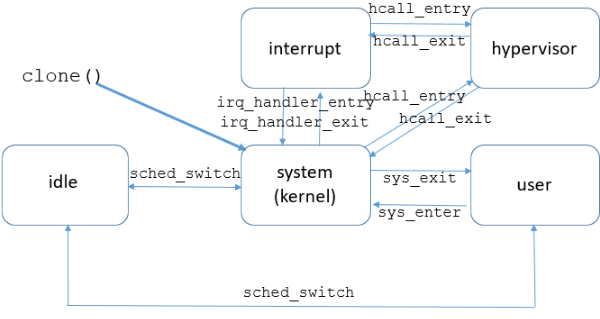
The most important point of the diagram is that there are events for each state transition.
- Task creation:
clonesystem call - Task termination:
sched:sched_process_exit - Task replacement:
sched:sched_process_exec - Task migration:
sched_setaffinitysystem call (explicit),sched:sched_migrate_task(implicit) - Task scheduling:
sched:sched_switch - System calls:
raw_syscalls:sys_enter,raw_syscalls:sys_exit - Hypervisor calls: (POWER-specific)
powerpc:hcall_entry,powerpc:hcall_exit - Interrupts:
irq:irq_handler_entry,irq:irq_handler_exit
The curt command for Linux
perf provides a suitable infrastructure with which to capture the necessary data for system utilization. There are a sufficient set of events available for tracing in the Linux kernel. The Python scripting capabilities permit a powerful and flexible means of processing the trace data. It's time to write the tool.
High-level design
In processing each event, the relevant state of the affected tasks must be updated:
- New task? Create and initialize data structures to track the task's state
- Command
- Process ID
- Task ID
- Migration count (0)
- Current CPU
- New CPU for this task? Create and initialize data structures for CPU-specific data
- User time (0)
- System time (0)
- Hypervisor time (0)
- Interrupt time (0)
- Idle time (0)
- New transaction for this task? Create and initialize data structures for transaction-specific data
- Elapsed time (0)
- Count (0)
- Minimum (maxint), maximum (0)
- Existing task?
- Accumulate time for the previous state
- Transaction ending? Accumulate time for the transaction, adjust minimum, maximum values
- Set new state
- Save current time (time current state entered)
- Migration? Increment migration count
High-level example
For a raw_syscalls:sys_enter event:
- If this task has not been seen before, allocate and initialize a new task data structure
- If the CPU is new for this task, allocate and initialize a new CPU data structure
- If this system call is new for this task, allocate and initialize a new call data structure
- In the task data structure:
- Accumulate the time since the last state change in a bucket for the current state ("user")
- Set the new state ("system")
- Save the current timestamp as the start of this time period for the new state
Edge cases
sys_exit as a task's first event
If the first event in the trace for a task is raw_syscalls:sys_exit:
- There is no matching
raw_syscalls:sys_enterwith which to determine the start time of this system call. - The accumulated time since the start of the trace was all spent in the system call and needs to be added to the overall elapsed time spent in all calls to this system call.
- The elapsed time of this system call is unknown.
- It would be inaccurate to account for this elapsed time in the average, minimum, or maximum statistics for this system call.
In this case, the tool creates a separate bucket called "pending" for time spent in the system call that cannot be accounted for in the average, minimum, or maximum.
A "pending" bucket is required for all transactional events (system calls, hypervisor calls, and interrupts).
sys_enter as a task's last event
Similarly, If the last event in the trace for a task is raw_syscalls:sys_enter:
- There is no matching
raw_syscalls:sys_exitwith which to determine the end time of this system call. - The accumulated time from the start of the system call to the end of the trace was all spent in the system call and needs to be added to the overall elapsed time spent in all calls to this system call.
- The elapsed time of this system call is unknown.
- It would be inaccurate to account for this elapsed time in the average, minimum, or maximum statistics for this system call.
This elapsed time is also accumulated in the "pending" bucket.
A "pending" bucket is required for all transactional events (system calls, hypervisor calls, and interrupts).
Since this condition can only be discovered at the end of the trace, a final "wrap-up" step is required in the tool where the statistics for all known tasks are completed based on their final states.
Indeterminable state
It is possible that a very busy task (or a short trace) will never see an event for a task from which the task's state can be determined. For example, if only sched:sched_switch or sched:sched_task_migrate events are seen for a task, it is impossible to determine that task's state. However, the task is known to exist and to be running.
Since the actual state cannot be determined, the runtime for the task is accumulated in a separate bucket, arbitrarily called "busy-unknown." For completeness, this time is also displayed in the final report.
Invisible tasks
For very, very busy tasks (or a short trace), it is possible that a task was actively running during the entire time the trace was being collected, but no events for that task appear in the trace. It was never migrated, paused, or forced to wait.
Such tasks cannot be known to exist by the tool and will not appear in the report.
curt.py Python classes
Task
- One per task
- Holds all task-specific data (command, process ID, state, CPU, list of CPU data structures [see below], migration count, lists of per-call data structures [see below])
- Maintains task state
Call
- One per unique transaction, per task (for example, one for the "open" system call, one for the "close" system call, one for IRQ 27, etc.)
- Holds call-specific data (e.g., start timestamp, count, elapsed time, minimum, maximum)
- Allocated as needed (lazy allocation)
- Stored within a task in a Python dictionary indexed by the unique identifier of the call (e.g., system call code, IRQ number, etc.)
CPU
- One per CPU on which this task has been observed to be running
- Holds per-CPU task data (e.g., user time, system time, hypervisor call time, interrupt time)
- Allocated as needed (lazy allocation)
- Stored within a task in a Python dictionary indexed by the CPU number
curt.py event processing example
As previously discussed, perf script will iterate over all events in the trace and call the appropriate event-handling function for each event.
A first attempt at an event-handling function for sys_exit, given the high-level example above, might be:
tasks = {}
def raw_syscalls__sys_enter(event_name, context, common_cpu, common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm, common_callchain, id, args):
# convert the multiple timestamp values into a single value
timestamp = nsecs(common_secs, common_nsecs)
# find this task's data structure
try:
task = tasks[common_pid]
except:
# new task!
task = Task()
# save the command string
task.comm = common_comm
# save the new task in the global list (dictionary) of tasks
tasks[common_pid] = task
if common_cpu not in task.cpus:
# new CPU!
task.cpu = common_cpu
task.cpus[common_cpu] = CPU()
# compute time spent in the previous state ('user')
delta = timestamp – task.timestamp
# accumulate 'user' time for this task/CPU
task.cpus[task.cpu].user += delta
if id not in task.syscalls:
# new system call for this task!
task.syscalls[id] = Call()
# change task's state
task.mode = 'sys'
# save the timestamp for the last event (this one) for this task
task.timestamp = timestamp
def raw_syscalls__sys_exit(event_name, context, common_cpu, common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm, common_callchain, id, ret):
# convert the multiple timestamp values into a single value
timestamp = nsecs(common_secs, common_nsecs)
# get the task data structure
task = tasks[common_pid]
# compute elapsed time for this system call
delta = task.timestamp - timestamp
# accumulate time for this task/system call
task.syscalls[id].elapsed += delta
# increment the tally for this task/system call
task.syscalls[id].count += 1
# adjust statistics
if delta < task.syscalls[id].min:
task.syscalls[id].min = delta
if delta > task.syscalls[id].max:
task.syscalls[id].max = delta
# accumulate time for this task's state on this CPU
task.cpus[common_cpu].system += delta
# change task's state
task.mode = 'user'
# save the timestamp for the last event (this one) for this task
task.timestamp = timestampHandling the edge cases
Following are some of the edge cases that are possible and must be handled.
Sys_exit as first event
As a system-wide trace can be started at an arbitrary time, it is certainly possible that the first event for a task is raw_syscalls:sys_exit. This requires adding the same code for new task discovery from the event-handling function for raw_syscalls:sys_enter to the handler for raw_syscalls:sys_exit. This:
# get the task data structure
task = tasks[common_pid]becomes this:
# find this task's data structure
try:
task = tasks[common_pid]
except:
# new task!
task = Task()
# save the command string
task.comm = common_comm
# save the new task in the global list (dictionary) of tasks
tasks[common_pid] = taskAnother issue is that it is impossible to properly accumulate the data for this system call since there is no timestamp for the start of the system call. The time from the start of the trace until this event has been spent by this task in the system call. It would be inaccurate to ignore this time. It would also be inaccurate to incorporate this time such that it is used to compute the average, minimum, or maximum. The only reasonable option is to accumulate this separately, calling it "pending" system time. To accurately compute this time, the timestamp of the first event of the trace must be known. Since any event could be the first event in the trace, every event must conditionally save its timestamp if it is the first event. A global variable is required:
start_timestamp = 0And every event-handling function must conditionally save its timestamp:
# convert the multiple timestamp values into a single value
timestamp = nsecs(common_secs, common_nsecs)
If start_timestamp = 0:
start_timestamp = timestampSo, the event-handling function for raw_syscalls:sys_exit becomes:
def raw_syscalls__sys_exit(event_name, context, common_cpu, common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm, common_callchain, id, ret):
# convert the multiple timestamp values into a single value
timestamp = nsecs(common_secs, common_nsecs)
If start_timestamp = 0:
start_timestamp = timestamp
# find this task's data structure
try:
task = tasks[common_pid]
# compute elapsed time for this system call
delta = task.timestamp - timestamp
# accumulate time for this task/system call
task.syscalls[id].elapsed += delta
# increment the tally for this task/system call
task.syscalls[id].count += 1
# adjust statistics
if delta < task.syscalls[id].min:
task.syscalls[id].min = delta
if delta > task.syscalls[id].max:
task.syscalls[id].max = delta
except:
# new task!
task = Task()
# save the command string
task.comm = common_comm
# save the new task in the global list (dictionary) of tasks
tasks[common_pid] = task
# compute elapsed time for this system call
delta = start_timestamp - timestamp
# accumulate time for this task/system call
task.syscalls[id].pending += delta
# accumulate time for this task's state on this CPU
task.cpus[common_cpu].system += delta
# change task's state
task.mode = 'user'
# save the timestamp for the last event (this one) for this task
task.timestamp = timestampSys_enter as last event
A similar issue to having sys_exit as the first event for a task is when sys_enter is the last event seen for a task. The time spent in the system call must be accumulated for completeness but can't accurately impact the average, minimum, nor maximum. This time will also be accumulated in for a separate "pending" state.
To accurately determine the elapsed time of the pending system call, from sys_entry to the end of the trace period, the timestamp of the final event in the trace file is required. Unfortunately, there is no way to know which event is the last event until that event has already been processed. So, all events must save their respective timestamps in a global variable.
It may be that many tasks are in the state where the last event seen for them was sys_enter. Thus, after the last event is processed, a final "wrap up" step is required to complete the statistics for those tasks. Fortunately, there is a trace_end function which is called by perf after the final event has been processed.
Last, we need to save the id of the system call in every sys_enter.
curr_timestamp = 0
def raw_syscalls__sys_enter(event_name, context, common_cpu, common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm, common_callchain, id, args):
# convert the multiple timestamp values into a single value
curr_timestamp = nsecs(common_secs, common_nsecs)
[…]
task.syscall = id
[…]
def trace_end():
for tid in tasks.keys():
task = tasks[tid]
# if this task ended while executing a system call
if task.mode == 'sys':
# compute the time from the entry to the system call to the end of the trace period
delta = curr_timestamp - task.timestamp
# accumulate the elapsed time for this system call
task.syscalls[task.syscall].pending += delta
# accumulate the system time for this task/CPU
task.cpus[task.cpu].sys += deltaMigrations
A task migration is when a task running on one CPU is moved to another CPU. This can happen by either:
- Explicit request (e.g., a call to
sched_setaffinity), or - Implicitly by the kernel (e.g., load balancing or vacating a CPU being taken offline)
When detected:
- The migration count for the task should be incremented
- The statistics for the previous CPU should be updated
- A new CPU data structure may need to be updated and initialized if the CPU is new for the task
- The task's current CPU is set to the new CPU
For accurate statistics, task migrations must be detected as soon as possible. The first case, explicit request, happens within a system call and can be detected in the sys_exit event for that system call. The second case has its own event, sched:sched_migrate_task, so it will need a new event-handling function.
def raw_syscalls__sys_exit(event_name, context, common_cpu, common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm, common_callchain, id, ret):
# convert the multiple timestamp values into a single value
timestamp = nsecs(common_secs, common_nsecs)
If start_timestamp = 0:
start_timestamp = timestamp
# find this task's data structure
try:
task = tasks[common_pid]
# compute elapsed time for this system call
delta = task.timestamp - timestamp
# accumulate time for this task/system call
task.syscalls[id].elapsed += delta
# increment the tally for this task/system call
task.syscalls[id].count += 1
# adjust statistics
if delta < task.syscalls[id].min:
task.syscalls[id].min = delta
if delta > task.syscalls[id].max:
task.syscalls[id].max = delta
except:
# new task!
task = Task()
# save the command string
task.comm = common_comm
# save the new task in the global list (dictionary) of tasks
tasks[common_pid] = task
task.cpu = common_cpu
# compute elapsed time for this system call
delta = start_timestamp - timestamp
# accumulate time for this task/system call
task.syscalls[id].pending += delta
If common_cpu != task.cpu:
task.migrations += 1
# divide the time spent in this syscall in half...
delta /= 2
# and give have to the previous CPU, below, and half to the new CPU, later
task.cpus[task.cpu].system += delta
# accumulate time for this task's state on this CPU
task.cpus[common_cpu].system += delta
# change task's state
task.mode = 'user'
# save the timestamp for the last event (this one) for this task
task.timestamp = timestamp
def sched__sched_migrate_task(event_name, context, common_cpu,
common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm,
common_callchain, comm, pid, prio, orig_cpu,
dest_cpu, perf_sample_dict):
If start_timestamp = 0:
start_timestamp = timestamp
# find this task's data structure
try:
task = tasks[common_pid]
except:
# new task!
task = Task()
# save the command string
task.comm = common_comm
# save the new task in the global list (dictionary) of tasks
tasks[common_pid] = task
task.cpu = common_cpu
If common_cpu not in task.cpus:
task.cpus[common_cpu] = CPU()
task.migrations += 1Task creation
To accurately collect statistics for a task, it is essential to know when the task is created. Tasks can be created with fork(), which creates a new process, or pthread_create(), which creates a new task within the same process. Fortunately, both are manifested by a clone system call and made evident by a sched:sched_process_fork event. The lifetime of the task starts at the sched_process_fork event. The edge case that arises is that the first likely events for the new task are:
sched_switchwhen the new task starts running. The new task should be considered idle at creation until this event occurssys_exitfor theclonesystem call. The initial state of the new task needs to be based on the state of the task that creates it, including being within theclonesystem call.
One edge case that must be handled is if the creating task (parent) is not yet known, it must be created and initialized, and the presumption is that it has been actively running since the start of the trace.
def sched__sched_process_fork(event_name, context, common_cpu,
common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm,
common_callchain, parent_comm, parent_pid, child_comm, child_pid):
global start_timestamp, curr_timestamp
curr_timestamp = self.timestamp
if (start_timestamp == 0):
start_timestamp = curr_timestamp
# find this task's data structure
try:
task = tasks[common_pid]
except:
# new task!
task = Task()
# save the command string
task.comm = common_comm
# save the new task in the global list (dictionary) of tasks
tasks[common_pid] = task
try:
parent = tasks[self.parent_tid]
except:
# need to create parent task here!
parent = Task(start_timestamp, self.command, 'sys', self.pid)
parent.sched_stat = True # ?
parent.cpu = self.cpu
parent.cpus[parent.cpu] = CPU()
tasks[self.parent_tid] = parent
task.resume_mode = parent.mode
task.syscall = parent.syscall
task.syscalls[task.syscall] = Call()
task.syscalls[task.syscall].timestamp = self.timestampTask exit
Similarly, for complete and accurate task statistics, it is essential to know when a task has terminated. There's an event for that: sched:sched_process_exit. This one is pretty easy to handle, in that the effort is just to close out the statistics and set the mode appropriately, so any end-of-trace processing will not think the task is still active:
def sched__sched_process_exit_old(event_name, context, common_cpu,
common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm,
common_callchain, comm, pid, prio):
global start_timestamp, curr_timestamp
curr_timestamp = self.timestamp
if (start_timestamp == 0):
start_timestamp = curr_timestamp
# find this task's data structure
try:
task = tasks[common_pid]
except:
# new task!
task = Task()
# save the command string
task.comm = common_comm
task.timestamp = curr_timestamp
# save the new task in the global list (dictionary) of tasks
tasks[common_pid] = task
delta = timestamp – task.timestamp
task.sys += delta
task.mode = 'exit'Output
What follows is an example of the report displayed by curt, slightly reformatted to fit on a narrower page width and with the idle-time classification data (which makes the output very wide) removed, and for brevity. Seen are two processes, 1497 and 2857. Process 1497 has two tasks, 1497 and 1523. Each task has a per-CPU summary and system-wide ("ALL" CPUs) summary. Each task's data is followed by the system call data for that task (if any), hypervisor call data (if any), and interrupt data (if any). After each process's respective tasks is a per-process summary. Process 2857 has a task 2857-0 that is the previous task image before an exec() system call replaced the process image. After all processes is a system-wide summary.
1497:
-- [ task] command cpu user sys irq hv busy idle | util% moves
[ 1497] X 2 0.076354 0.019563 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 15.818719 | 0.6%
[ 1497] X ALL 0.076354 0.019563 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 15.818719 | 0.6% 0
-- ( ID)name count elapsed pending average minimum maximum
( 0)read 2 0.004699 0.000000 0.002350 0.002130 0.002569
(232)epoll_wait 1 9.968375 5.865208 9.968375 9.968375 9.968375
-- [ task] command cpu user sys irq hv busy idle | util% moves
[ 1523] InputThread 1 0.052598 0.037073 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 15.824965 | 0.6%
[ 1523] InputThread ALL 0.052598 0.037073 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 15.824965 | 0.6% 0
-- ( ID)name count elapsed pending average minimum maximum
( 0)read 14 0.011773 0.000000 0.000841 0.000509 0.002185
( 1)write 2 0.010763 0.000000 0.005381 0.004974 0.005789
(232)epoll_wait 1 9.966649 5.872853 9.966649 9.966649 9.966649
-- [ task] command cpu user sys irq hv busy idle | util% moves
[ ALL] ALL 0.128952 0.056636 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 31.643684 | 0.6% 0
2857:
-- [ task] command cpu user sys irq hv busy idle | util% moves
[ 2857] execs.sh 1 0.257617 0.249685 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.266200 | 65.6%
[ 2857] execs.sh 2 0.000000 0.023951 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.005728 | 80.7%
[ 2857] execs.sh 5 0.313509 0.062271 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.344279 | 52.2%
[ 2857] execs.sh 6 0.136623 0.128883 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.533263 | 33.2%
[ 2857] execs.sh 7 0.527347 0.194014 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.990625 | 42.1%
[ 2857] execs.sh ALL 1.235096 0.658804 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 2.140095 | 46.9% 4
-- ( ID)name count elapsed pending average minimum maximum
( 9)mmap 15 0.059388 0.000000 0.003959 0.001704 0.017919
( 14)rt_sigprocmask 12 0.006391 0.000000 0.000533 0.000431 0.000711
( 2)open 9 2.253509 0.000000 0.250390 0.008589 0.511953
( 3)close 9 0.017771 0.000000 0.001975 0.000681 0.005245
( 5)fstat 9 0.007911 0.000000 0.000879 0.000683 0.001182
( 10)mprotect 8 0.052198 0.000000 0.006525 0.003913 0.018073
( 13)rt_sigaction 8 0.004281 0.000000 0.000535 0.000458 0.000751
( 0)read 7 0.197772 0.000000 0.028253 0.000790 0.191028
( 12)brk 5 0.003766 0.000000 0.000753 0.000425 0.001618
( 8)lseek 3 0.001766 0.000000 0.000589 0.000469 0.000818
-- [ task] command cpu user sys irq hv busy idle | util% moves
[2857-0] perf 6 0.053925 0.191898 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.827263 | 22.9%
[2857-0] perf 7 0.000000 0.656423 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.484107 | 57.6%
[2857-0] perf ALL 0.053925 0.848321 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 1.311370 | 40.8% 1
-- ( ID)name count elapsed pending average minimum maximum
( 0)read 0 0.000000 0.167845 -- -- --
( 59)execve 0 0.000000 0.000000 -- -- --
ALL:
-- [ task] command cpu user sys irq hv busy idle | util% moves
[ ALL] ALL 10.790803 29.633170 0.160165 0.000000 0.137747 54.449823 | 7.4% 50
-- ( ID)name count elapsed pending average minimum maximum
( 1)write 2896 1.623985 0.000000 0.004014 0.002364 0.041399
(102)getuid 2081 3.523861 0.000000 0.001693 0.000488 0.025157
(142)sched_setparam 691 7.222906 32.012841 0.024925 0.002024 0.662975
( 13)rt_sigaction 383 0.235087 0.000000 0.000614 0.000434 0.014402
( 8)lseek 281 0.169157 0.000000 0.000602 0.000452 0.013404
( 0)read 133 2.782795 0.167845 0.020923 0.000509 1.864439
( 7)poll 96 8.583354 131.889895 0.193577 0.000626 4.596280
( 4)stat 93 7.036355 1.058719 0.183187 0.000981 3.661659
( 47)recvmsg 85 0.146644 0.000000 0.001725 0.000646 0.019067
( 3)close 79 0.171046 0.000000 0.002165 0.000428 0.020659
( 9)mmap 78 0.311233 0.000000 0.003990 0.001613 0.017919
(186)gettid 74 0.067315 0.000000 0.000910 0.000403 0.014075
( 2)open 71 3.081589 0.213059 0.184248 0.001921 0.937946
(202)futex 62 5.145112 164.286154 0.405566 0.000597 11.587437
-- ( ID)name count elapsed pending average minimum maximum
( 12)i8042 10 0.160165 0.000000 0.016016 0.010920 0.032805
Total Trace Time: 15.914636 msHurdles and issues
Following are some of the issues encountered in the development of curt.
Out-of-order events
One of the more challenging issues is the discovery that events in a perf.data file can be out of time order. For a program trying to monitor state transitions carefully, this is a serious issue. For example, a trace could include the following sequence of events, displayed as they appear in the trace file:
time 0000: sys_enter syscall1
time 0007: sys_enter syscall2
time 0006: sys_exit syscall1
time 0009: sys_exit syscall2Just blindly processing these events in the order they are presented to their respective event-handling functions (in the wrong time order) will result in incorrect statistics (or worse).
The most user-friendly ways to handle out-of-order events include:
- Prevent traces from having out-of-order events in the first place by changing the way
perf recordworks - Providing a means to reorder events in a trace file, perhaps by enhancing
perf inject - Modifying how
perf scriptworks to present the events to the event-handling functions in time order
But user-friendly is not the same as straightforward, nor easy. Also, none of the above are in the user's control.
I chose to implement a queue for incoming events that would be sufficiently deep to allow for proper reordering of all events. This required a significant redesign of the code, including implementation of classes for each event, and moving the event processing for each event type into a method in that event's class.
In the redesigned code, the actual event handlers' only job is to save the relevant data from the event into an instance of the event class, queue it, then process the top (oldest in time) event from the queue:
def raw_syscalls__sys_enter(event_name, context, common_cpu, common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm, common_callchain, id, args):
event = Event_sys_enter(nsecs(common_secs,common_nsecs), common_cpu, common_pid, common_comm, id)
process_event(event)The simple reorderable queuing mechanism is in a common function:
events = []
n_events = 0
def process_event(event):
global events,n_events,curr_timestamp
i = n_events
while i > 0 and events[i-1].timestamp > event.timestamp:
i = i-1
events.insert(i,event)
if n_events < params.window:
n_events = n_events+1
else:
event = events[0]
# need to delete from events list now,
# because event.process() could reenter here
del events[0]
if event.timestamp < curr_timestamp:
sys.stderr.write("Error: OUT OF ORDER events detected.\n Try increasing the size of the look-ahead window with --window=<n>\n")
event.process()Note that the size of the queue is configurable, primarily for performance and to limit memory consumption. The function will report when that queue size is insufficient to eliminate out-of-order events. It is worth considering whether to consider this case a catastrophic failure and elect to terminate the program.
Implementing a class for each event type led to some consideration for refactoring, such that common code could coalesce into a base class:
class Event (object):
def __init__(self):
self.timestamp = 0
self.cpu = 0
self.tid = 0
self.command = 'unknown'
self.mode = 'unknown'
self.pid = 0
def process(self):
global start_timestamp
try:
task = tasks[self.tid]
if task.pid == 'unknown':
tasks[self.tid].pid = self.pid
except:
task = Task(start_timestamp, self.command, self.mode, self.pid)
tasks[self.tid] = task
if self.cpu not in task.cpus:
task.cpus[self.cpu] = CPU()
if task.cpu == 'unknown':
task.cpu = self.cpu
if self.cpu != task.cpu:
task.cpu = self.cpu
task.migrations += 1
return taskThen a class for each event type would be similarly constructed:
class Event_sys_enter ( Event ):
def __init__(self, timestamp, cpu, tid, comm, id, pid):
self.timestamp = timestamp
self.cpu = cpu
self.tid = tid
self.command = comm
self.id = id
self.pid = pid
self.mode = 'busy-unknown'
def process(self):
global start_timestamp, curr_timestamp
curr_timestamp = self.timestamp
if (start_timestamp == 0):
start_timestamp = curr_timestamp
task = super(Event_sys_enter, self).process()
if task.mode == 'busy-unknown':
task.mode = 'user'
for cpu in task.cpus:
task.cpus[cpu].user = task.cpus[cpu].busy_unknown
task.cpus[cpu].busy_unknown = 0
task.syscall = self.id
if self.id not in task.syscalls:
task.syscalls[self.id] = Call()
task.syscalls[self.id].timestamp = curr_timestamp
task.change_mode(curr_timestamp, 'sys')Further refactoring is evident above, as well, moving the common code that updates relevant statistics based on a task's state change and the state change itself into a change_mode method of the Task class.
Start-of-trace timestamp
As mentioned above, for scripts that depend on elapsed time, there should be an easier way to get the first timestamp in the trace other than forcing every event-handling function to conditionally save its timestamp as the start-of-trace timestamp.
Awkward invocation
The syntax for invoking a perf Python script, including script parameters, is slightly awkward:
$ perf script –s ./curt.py -- --window=80Also, it's awkward that perf Python scripts are not themselves executable.
The curt.py script was made directly executable and will invoke perf, which will in turn invoke the script. Implementation is a bit confusing but it's easy to use:
$ ./curt.py --window=80This script must detect when it has been directly invoked. The Python environment established by perf is a virtual module from which the perf Python scripts import:
try:
from perf_trace_context import *If this import fails, the script was directly invoked. In this case, the script will exec perf, specifying itself as the script to run, and passing along any command line parameters:
except:
if len(params.file_or_command) == 0:
params.file_or_command = [ "perf.data" ]
sys.argv = ['perf', 'script', '-i' ] + params.file_or_command + [ '-s', sys.argv[0] ]
sys.argv.append('--')
sys.argv += ['--window', str(params.window)]
if params.debug:
sys.argv.append('--debug')
sys.argv += ['--api', str(params.api)]
if params.debug:
print sys.argv
os.execvp("perf", sys.argv)
sys.exit(1)In this way, the script can not only be run directly, it can still be run by using the perf script command.
Simultaneous event registration required
An artifact of the way perf enables events can lead to unexpected trace data. For example, specifying:
$ perf record –a –e raw_syscalls:sys_enter –e raw_syscalls:sys_exit ./commandWill result in a trace file that begins with the following series of events for a single task (the perf command itself):
sys_enter
sys_enter
sys_enter
…This happens because perf will register the sys_enter event for every CPU on the system (because of the -a argument), then it will register the sys_exit event for every CPU. In the latter case, since the sys_enter event has already been enabled for each CPU, that event shows up in the trace; but since the sys_exit has not been enabled on each CPU until after the call returns, the sys_exit call does not show up in the trace. The reverse issue happens at the end of the trace file, with a series of sys_exit events in the trace because the sys_enter event has already been disabled.
The solution to this issue is to group the events, which is not well documented:
$ perf record –e '{raw_syscalls:sys_enter,raw_syscalls:sys_exit}' ./commandWith this syntax, the sys_enter and sys_exit events are enabled simultaneously.
Awkward recording step
There are a lot of different events required for computation of the full set of statistics for tasks. This leads to a very long, complicated command for recording:
$ perf record -e '{raw_syscalls:*,sched:sched_switch,sched:sched_migrate_task,sched:sched_process_exec,sched:sched_process_fork,sched:sched_process_exit,sched:sched_stat_runtime,sched:sched_stat_wait,sched:sched_stat_sleep,sched:sched_stat_blocked,sched:sched_stat_iowait,powerpc:hcall_entry,powerpc:hcall_exit}' -a *command --args*The solution to this issue is to enable the script to perform the record step itself, by itself invoking perf. A further enhancement is to proceed after the recording is complete and report the statistics from that recording:
if params.record:
# [ed. Omitting here the list of events for brevity]
eventlist = '{' + eventlist + '}' # group the events
command = ['perf', 'record', '--quiet', '--all-cpus',
'--event', eventlist ] + params.file_or_command
if params.debug:
print command
subprocess.call(command)The command syntax required to record and report becomes:
$ ./curt.py --record ./commandProcess IDs and perf API change
Process IDs are treated a bit cavalierly by perf scripting. Note well above that one of the common parameters for the generated event-handling functions is named common_pid. This is not the process ID, but the task ID. In fact, on many current Linux-based distributions, there is no way to determine a task's process ID from within a perf Python script. This presents a serious problem for a script that wants to compute statistics for a process.
Fortunately, in Linux kernel v4.14, an additional parameter was provided to each of the event-handling functions—perf_sample_dict—a dictionary from which the process ID could be extracted: (perf_sample_dict['sample']['pid']).
Unfortunately, current Linux distributions may not have that version of the Linux kernel. If the script is written to expect that extra parameter, the script will fail and report an error:
TypeError: irq__irq_handler_exit_new() takes exactly 11 arguments (10 given)Ideally, a means to automatically discover if the additional parameter is passed would be available to permit a script to easily run with both the old and new APIs and to take advantage of the new API if it is available. Unfortunately, such a means is not readily apparent.
Since there is clearly value in using the new API to determine process-wide statistics, curt provides a command line option to use the new API. curt then takes advantage of Python's lazy function binding to adjust, at run-time, which API to use:
if params.api == 1:
dummy_dict = {}
dummy_dict['sample'] = {}
dummy_dict['sample']['pid'] = 'unknown'
raw_syscalls__sys_enter = raw_syscalls__sys_enter_old
[…]
else:
raw_syscalls__sys_enter = raw_syscalls__sys_enter_new
[…]This requires two functions for each event:
def raw_syscalls__sys_enter_new(event_name, context, common_cpu, common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm, common_callchain, id, args, perf_sample_dict):
event = Event_sys_enter(nsecs(common_secs,common_nsecs), common_cpu, common_pid, common_comm, id, perf_sample_dict['sample']['pid'])
process_event(event)
def raw_syscalls__sys_enter_old(event_name, context, common_cpu, common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm, common_callchain, id, args):
global dummy_dict
raw_syscalls__sys_enter_new(event_name, context, common_cpu, common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm, common_callchain, id, args, dummy_dict)Note that the event-handling function for the older API will make use of the function for the newer API, passing a statically defined dictionary containing just enough data such that accessing it as perf_sample_dict['sample']['pid'] will work (resulting in 'unknown').
Events reported on other CPUs
Not all events that refer to a task are reported from a CPU on which the task is running. This could result in an artificially high migration count and other incorrect statistics. For these types of events (sched_stat), the event CPU is ignored.
Explicit migrations (no sched_migrate event)
While there is conveniently an event for when the kernel decides to migrate a task from one CPU to another, there is no event for when the task requests a migration on its own. These are effected by system calls (sched_setaffinity), so the sys_exit event handler must compare the event CPU to the task's CPU, and if different, presume a migration has occurred. (This is described above, but repeated here in the "issues" section for completeness.)
Mapping system call IDs to names is architecture-specific
System calls are identified in events only as unique numeric identifiers. These identifiers are not readily interpreted by humans in the report. These numeric identifiers are not readily mapped to their mnemonics because they are architecture-specific, and new system calls can be added in newer kernels. Fortunately, perf provides a means to map system call numeric identifiers to system call names. A simple example follows:
from Util import syscall_name
def raw_syscalls__sys_enter(event_name, context, common_cpu,
common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm,
common_callchain, id, args, perf_sample_dict):
print "%s id=%d" % (syscall_name(id), id)Unfortunately, using syscall_name introduces a dependency on the audit python bindings. This dependency is being removed in upstream versions of perf.
Mapping hypervisor call IDs to names is non-existent
Similar to system calls, hypervisor calls are also identified only with numeric identifiers. For IBM's POWER hypervisor, they are statically defined. Unfortunately, perf does not provide a means to map hypervisor call identifiers to mnemonics. curt includes a (hardcoded) function to do just that:
hcall_to_name = {
'0x4':'H_REMOVE',
'0x8':'H_ENTER',
'0xc':'H_READ',
'0x10':'H_CLEAR_MOD',
[…]
}
def hcall_name(opcode):
try:
return hcall_to_name[hex(opcode)]
except:
return str(opcode)Command strings as bytearrays
perf stores command names and string arguments in Python bytearrays. Unfortunately, printing bytearrays in Python prints every character in the bytearray—even if the string is null-terminated. For example:
$ perf record –a –e 'sched:sched_switch' sleep 3
$ perf script –g Python
generated Python script: perf-script.py
$ perf script -s ./perf-script.py
in trace_begin
sched__sched_switch 3 664597.912692243 21223 perf prev_comm=perf^@-terminal-^@, prev_pid=21223, prev_prio=120, prev_state=, next_comm=migration/3^@^@^@^@^@, next_pid=23, next_prio=0
[…]One solution is to truncate the length of these bytearrays based on null termination, as needed before printing:
def null(ba):
null = ba.find('\x00')
if null >= 0:
ba = ba[0:null]
return ba
def sched__sched_switch(event_name, context, common_cpu,
common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm,
common_callchain, prev_comm, prev_pid, prev_prio, prev_state,
next_comm, next_pid, next_prio, perf_sample_dict):
print "prev_comm=%s, prev_pid=%d, prev_prio=%d, " \
"prev_state=%s, next_comm=%s, next_pid=%d, " \
"next_prio=%d" % \
(null(prev_comm), prev_pid, prev_prio,
flag_str("sched__sched_switch", "prev_state", prev_state),
null(next_comm), next_pid, next_prio)Which nicely cleans up the output:
sched__sched_switch 3 664597.912692243 21223 perf prev_comm=perf, prev_pid=21223, prev_prio=120, prev_state=, next_comm=migration/3, next_pid=23, next_prio=0Dynamic mappings, like IRQ number to name
Dissimilar to system calls and hypervisor calls, interrupt numbers (IRQs) are dynamically assigned by the kernel on demand, so there can't be a static table mapping an IRQ number to a name. Fortunately, perf passes the name to the event's irq_handler_entry routine. This allows a script to create a dictionary that maps the IRQ number to a name:
irq_to_name = {}
def irq__irq_handler_entry_new(event_name, context, common_cpu, common_secs, common_nsecs, common_pid, common_comm, common_callchain, irq, name, perf_sample_dict):
irq_to_name[irq] = name
event = Event_irq_handler_entry(nsecs(common_secs,common_nsecs), common_cpu, common_pid, common_comm, irq, name, getpid(perf_sample_dict))
process_event(event)Somewhat oddly, perf does not pass the name to the irq_handler_exit routine. So, it is possible that a trace may only see an irq_handler_exit for an IRQ and must be able to tolerate that. Here, instead of mapping the IRQ to a name, the IRQ number is returned as a string instead:
def irq_name(irq):
if irq in irq_to_name:
return irq_to_name[irq]
return str(irq)Task 0
Task 0 shows up everywhere. It's not a real task. It's a substitute for the "idle" state. It's the task ID given to the sched_switch event handler when the CPU is going to (or coming from) the "idle" state. It's often the task that is "interrupted" by interrupts. Tracking the statistics for task 0 as if it were a real task would not make sense. Currently, curt ignores task 0. However, this loses some information, like some time spent in interrupt processing. curt should, but currently doesn't, track interesting (non-idle) time for task 0.
Spurious sched_migrate_task events (same CPU)
Rarely, a sched_migrate_task event occurs in which the source and target CPUs are the same. In other words, the task is not migrated. To avoid artificially inflated migration counts, this case must be explicitly ignored:
class Event_sched_migrate_task (Event):
def process(self):
[…]
if self.cpu == self.dest_cpu:
returnexec
The semantics of the exec system call are that the image of the current process is replaced by a completely new process image without changing the process ID. This is awkward for tracking the statistics of a process (really, a task) based on the process (task) ID. The change is significant enough that the statistics for each task should be accumulated separately, so the current task's statistics need to be closed out and a new set of statistics should be initialized. The challenge is that both the old and new tasks have the same process (task) ID. curt addresses this by tagging the task's task ID with a numeric suffix:
class Event_sched_process_exec (Event):
def process(self):
global start_timestamp, curr_timestamp
curr_timestamp = self.timestamp
if (start_timestamp == 0):
start_timestamp = curr_timestamp
task = super(Event_sched_process_exec, self).process()
new_task = Task(self.timestamp, self.command, task.mode, self.pid)
new_task.sched_stat = True
new_task.syscall = task.syscall
new_task.syscalls[task.syscall] = Call()
new_task.syscalls[task.syscall].timestamp = self.timestamp
task.change_mode(curr_timestamp, 'exit')
suffix=0
while True:
old_tid = str(self.tid)+"-"+str(suffix)
if old_tid in tasks:
suffix += 1
else:
break
tasks[old_tid] = tasks[self.tid]
del tasks[self.tid]
tasks[self.tid] = new_taskThis will clearly separate the statistics for the different process images. In the example below, the perf command (task "9614-0") exec'd exec.sh (task "9614-1"), which in turn exec'd itself (task "9614"):
-- [ task] command cpu user sys irq hv busy idle | util% moves
[ 9614] execs.sh 4 1.328238 0.485604 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 2.273230 | 44.4%
[ 9614] execs.sh 7 0.000000 0.201266 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.003466 | 98.3%
[ 9614] execs.sh ALL 1.328238 0.686870 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 2.276696 | 47.0% 1
-- [ task] command cpu user sys irq hv busy idle | util% moves
[9614-0] perf 3 0.000000 0.408588 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 2.298722 | 15.1%
[9614-0] perf 4 0.059079 0.028269 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.611355 | 12.5%
[9614-0] perf 5 0.000000 0.067626 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.004702 | 93.5%
[9614-0] perf ALL 0.059079 0.504483 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 2.914779 | 16.2% 2
-- [ task] command cpu user sys irq hv busy idle | util% moves
[9614-1] execs.sh 3 1.207972 0.987433 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 2.435908 | 47.4%
[9614-1] execs.sh 4 0.000000 0.341152 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.004147 | 98.8%
[9614-1] execs.sh ALL 1.207972 1.328585 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 2.440055 | 51.0% 1Distribution support
Surprisingly, there is currently no support for perf's Python bindings in Ubuntu. Follow the saga for more detail.
Limit on number of traced events
As curt gets more sophisticated, it is likely that more and more events may be required to be included in the trace file. perf currently requires one file descriptor per event per CPU. This becomes a problem when the maximum number of open file descriptors is not a large multiple of the number of CPUs on the system. On systems with large numbers of CPUs, this quickly becomes a problem. For example, the default maximum number of open file descriptors is often 1,024. An IBM POWER8 system with four sockets may have 12 cores per socket and eight threads (CPUs) per core. Such a system has 4 * 12 * 8 = 392 CPUs. In that case, perf could trace only about two events! A workaround is to (significantly) increase the maximum number of open file descriptors (ulimit –n if the system administrator has configured the hard limits high enough; or the administrator can set the limits higher in /etc/security/limits.conf for nofile).
Summary
I hope this article shows the power of perf—and specifically the utility and flexibility of the Python scripting enabled with perf—to perform sophisticated processing of kernel trace data. Also, it shows some of the issues and edge cases that can be encountered when the boundaries of such technologies are tested.
Please feel free to download and make use of the curt tool described here, report problems, suggest improvements, or contribute code of your own on the curt GitHub page.







Comments are closed.