Like almost everyone on the planet, I have a few social media accounts. I mostly stick to Facebook to stay up to date with friends and family and Twitter to follow a few other people.
Have you ever wanted to make a post that includes italics or some other fancy formatting? You can easily change the text to italics or bold when you're writing an email, but most social media platforms don't provide many formatting options.
And sometimes, I just want to put a little emphasis into what I'm writing. If I've had a really good day and I want to share that with my friends, I might want to put that text in italics. For other posts, I might want to use different formatting that will help my text stand out. Sure, you can use emoji, but sometimes a little text formatting can add that extra pizzazz to your posts.
I found a way to do just that. With a short Gawk script I wrote, I can create fancy formatting that I can copy and paste into my social media posts.
Special HTML
HTML includes a bunch of special characters for mathematics, symbols, and other languages that most people are not aware of. Within the Mathematical Markup Language (MathML) math character support, HTML includes alternate versions of the alphabet for script, fraktur, and double-strike (shown respectively in this image) characters.
You can use these alternate versions of the alphabet to create fancy text.
The script alphabet variation is written as the letter followed by scr. Characters can be uppercase or lowercase. For example, to print the script letter a in an HTML page, type 𝒶, and to print the script letter Z in HTML, type 𝒵.
The fraktur and double-strike variations are referenced in similar ways. The fraktur mathematical lower-case a is 𝔞, and the capital Y is 𝔜. The mathematical double-strike a is referenced as 𝕒, and the double-strike X is 𝕏.
Gawk functions
Once you know how to reference the alternate versions of each letter, it's easy to define a few Gawk functions to print those HTML entities. Since these alternate characters exist only for letters and not punctuation or numbers, start with a simple wrapper function to determine if a character is an uppercase or lowercase letter.
#!/usr/bin/gawk -f
# Echo the input as different "fonts." Redirect this into an html
# page and copy/paste fancy text into twitter or facebook.
BEGIN { alpha="abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; }
function is_alpha(c) {
return(index(alpha, c));
}The BEGIN statement defines an alphabet string called alpha that contains all letters a–z and A–Z. The is_alpha(c) function uses the built-in index() function to return the location of the character c in the string alpha. If the character c is not a letter, index() returns zero, which the script uses as a False value.
Because the is_alpha(c) function just "wraps" a call to the index() function without doing anything else; this is called a wrapper function. Think of it as shorthand that makes the Gawk script easier to read.
With that, it's easy to define a few functions that convert single letters into each of the alternate versions of the alphabet. In general, each function calls is_alpha(c) to determine if a character is a letter a–z or A–Z. If it is (i.e., if the returned value is non-zero), then the function prints the HTML entity for that letter as script, fraktur, and double-strike. Otherwise, the function prints the letter.
function print_script(c) {
if ( is_alpha(c) ) { printf("&%cscr;", c); } else { printf("%c", c); }
}
function print_fraktur(c) {
if ( is_alpha(c) ) { printf("&%cfr;", c); } else { printf("%c", c); }
}
function print_double(c) {
if ( is_alpha(c) ) { printf("&%copf;", c); } else { printf("%c", c); }
}The print_script(c) function prints a single letter in script. Similarly, the print_fraktur(c) function prints a letter in fraktur, and the print_double(c) function prints a single letter in double-strike.
All that's left is a Gawk loop to convert plain text into each of the alternate alphabet characters. This script loops over each line three times and prints the text in script, fraktur, or double-strike. Each line is wrapped in <p> and </p> HTML tags.
{ text=$0;
len=length(text);
print "<p>";
for (i=1; i<=len; i++) {
print_script( substr(text, i, 1) );
}
print "</p><p>";
for (i=1; i<=len; i++) {
print_fraktur( substr(text, i, 1) );
}
print "</p><p>";
for (i=1; i<=len; i++) {
print_double( substr(text, i, 1) );
}
print "</p>";
}Putting it all together
I saved the above lines in a script file called htmlecho and put it in my ~/bin directory.
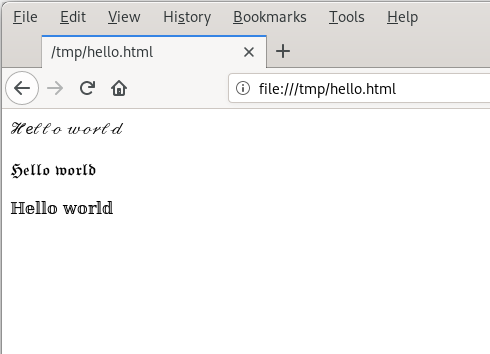
$ htmlecho > /tmp/hello.html
Hello world
^ZWhenever I want to add fancy text to my Facebook and Twitter posts, I just run the script and save the output to a temporary HTML page. I open the temporary page in a web browser and copy and paste the fancy text I like best into my social media posts.







1 Comment