I run Linux as my primary operating system, and I boot FreeDOS in a virtual machine. Most of the time, I use QEMU as my PC emulator, but sometimes I'll run other experiments with GNOME Boxes (which uses QEMU as a back-end virtual machine) or with VirtualBox.
I like to play classic DOS games, and sometimes I'll bring up a favorite DOS application. I teach a Management Information Systems (MIS) class where I talk about the history of computing, and I'll sometimes record a demonstration using FreeDOS and a legacy DOS application, such as As-Easy-As (my favorite DOS spreadsheet—once released as "shareware" but now available for free from TRIUS, Inc).
But using FreeDOS this way means I need to transfer files between my FreeDOS virtual machine and my Linux desktop system. Let me show you how I do that.
Accessing the image with guestmount
I used to access my virtual disk image by calculating the offset to the first DOS partition, then calling the Linux mount command with the right mix of options to match that offset. This was always error-prone and not very flexible. Fortunately, there's an easier way to do it. The guestmount program from the libguestfs-tools package lets you access or mount the virtual disk image from Linux. You can install libguestfs-tools using this command on Fedora:
$ yum install libguestfs-tools libguestfsUsing guestmount is not as easy as double-clicking the file from the GNOME file manager, but the command line isn't too difficult to use. The basic usage of guestmount is:
$ guestmount -a image -m device mountpointIn this usage, image is the virtual disk image to use. On my system, I created my QEMU virtual disk image with the qemu-img command. The guestmount program can read this disk image format, as well as the QCOW2 image format used by GNOME Boxes, or the VDI image format used in VirtualBox.
The device option indicates the partition on the virtual disk. Imagine using this virtual disk as a real hard drive. You would access the first partition as /dev/sda1, the second partition as /dev/sda2, and so on. That's the syntax for guestmount. By default, FreeDOS 1.3 RC4 creates one partition on an empty drive, so access that partition as /dev/sda1.
And mountpoint is the location to "mount" the DOS filesystem on your local Linux system. I'll usually create a temporary directory to work with. You only need the mount point while you're accessing the virtual disk.
Putting that all together, I use this set of commands to access my FreeDOS virtual disk image from Linux:
$ mkdir /tmp/freedos
$ guestmount -a freedos.img -m /dev/sda1 /tmp/freedosAfter that, I can access my FreeDOS files via the /tmp/freedos directory, using normal tools on Linux. I might use ls /tmp/freedos at the command line, or open the /tmp/freedos mount point using the desktop file manager.
$ ls -l /tmp/freedos
total 216
drwxr-xr-x. 5 root root 8192 May 10 15:53 APPS
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 85048 Apr 30 07:54 COMMAND.COM
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 103 May 13 15:48 CONFIG.SYS
drwxr-xr-x. 5 root root 8192 May 15 16:52 DEVEL
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 8192 May 15 13:36 EDLIN
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 1821 May 10 15:57 FDAUTO.BAT
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 740 May 13 15:47 FDCONFIG.SYS
drwxr-xr-x. 10 root root 8192 May 10 15:49 FDOS
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 46685 Apr 30 07:54 KERNEL.SYS
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 8192 May 10 15:57 SRC
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 3190 May 16 08:34 SRC.ZIP
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 8192 May 11 18:33 TEMP
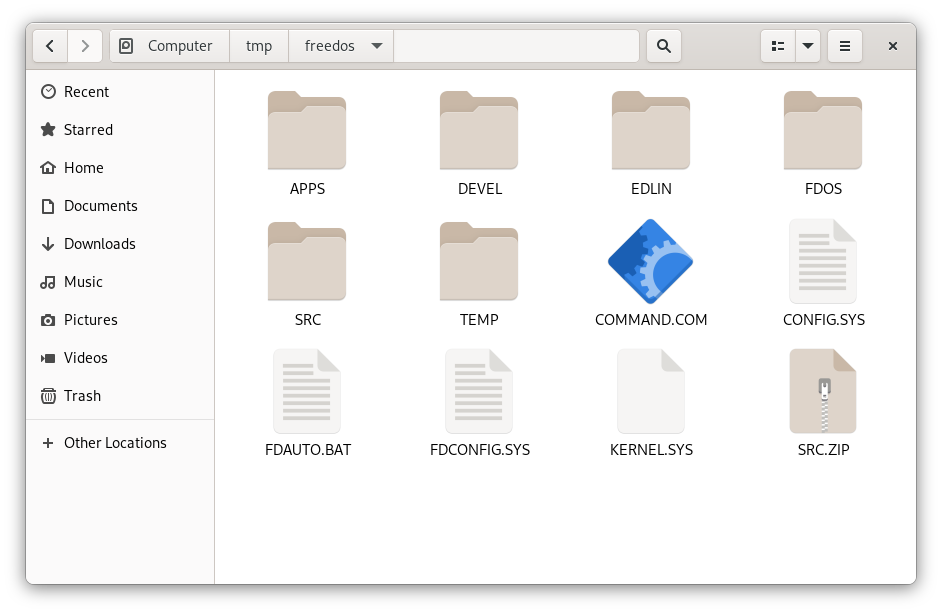
Using GNOME file manager to access the virtual disk
(Jim Hall, CC-BY SA 4.0)
For example, to copy several C source files from my Linux projects directory into C:\SRC on the virtual disk image, so I can use the files under FreeDOS later, I can use the Linux cp command:
$ cp /home/jhall/projects/*.c /tmp/freedos/SRCThe files and directories on the virtual drive are technically case insensitive, so you can refer to them using uppercase or lowercase letters. However, I find it more natural to type DOS files and directories using all uppercase.
$ ls /tmp/freedos
APPS CONFIG.SYS EDLIN FDCONFIG.SYS KERNEL.SYS SRC.ZIP
COMMAND.COM DEVEL FDAUTO.BAT FDOS SRC TEMP
$ ls /tmp/freedos/EDLIN
EDLIN.EXE MAKEFILE.OW
$ ls /tmp/freedos/edlin
EDLIN.EXE MAKEFILE.OW
Unmounting with guestmount
You should always unmount the virtual disk image before you use it again in your virtual machine. If you leave the image mounted while you run QEMU or VirtualBox, you risk messing up your files.
The companion command to guestmount is guestunmount, to unmount the disk image. Just give the mount point that you wish to unmount:
$ guestunmount /tmp/freedosNote that this command is spelled slightly differently from the Linux umount system command.


















Comments are closed.